Australlite
Introduction
Utilizing the announced Lower Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites constellations of OneWeb, SpaceX, LeoSat & Samsung to provide high speed connectivity to entire Australian continent with performance better than fiber networks. This project can eliminate high cost NBN roll out to scattered populations and will considerably improve disaster management. Providing high speed connectivity for mobile communication, internet, high resolution TV broadcast as well as utilizing technologies like IoT & Cloud for improvement in security, education, health, agriculture, livestock farming, mineral resources, wildlife, and environment without any coverage black-spots. This network will not require any infrastructure installations and will help the Government to generate revenues by issuing spectrum licenses to local as well as foreign investors for providing services directly to the end user.
2011 Census
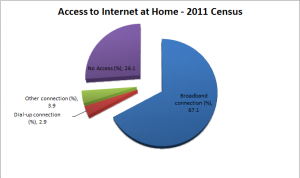
Source: Regional Statistics by ASGS, 2010-2014
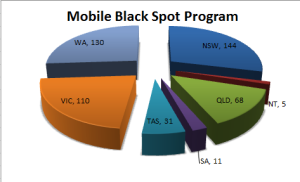
Mobile Black Spot Program
The Australian Government’s $100 million Mobile Black Spot Program will deliver almost 500 new or upgraded mobile base stations around Australia

Source: https://data.gov.au/dataset/mobile-black-spot-programme-funded-base-stations
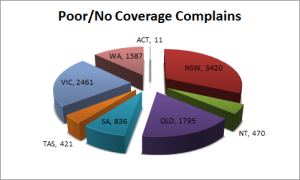
No or Poor Coverage
The Department of Communications and the Arts has received 10802 nominations of regional locations with poor or no mobile coverage from members of the public

Source: https://data.gov.au/dataset/community-reports-of-poor-or-no-mobile-coverage
Result
Scattered population, mainly based on the coastal areas with thousands of kilometers travel between big cities makes Australia prone to such area specific connectivity. This makes Australia a country of multiple virtual scattered islands.
Challenges
- Australia still lags behind every developed as well as many developing countries in terms of network availability and quality
- Rolling out fiber, copper, microwave and even traditional satellite communication networks are expensive and require infrastructure installations
- World of technology is developing every passing moment and amount of data communicated is increasing exponentially due to growth of technologies like; IoT, Cloud, HD TV, UHD TV, VR, AI etc. Current networks won’t be able to match this growth
- Being the guardian of Antarctica and Great Barrier Reef, monitoring wildlife, environment, and marine life in real time is Australia’s responsibility. Again heavy costs and infrastructure requirements limit these observations
- Disaster management in real time without dependency on infrastructure in remote regions
- Managing agricultural farms, livestock monitoring in larger areas in real time
- Education and health services in remote areas at lower costs
- Broadcasting HD, UHD, 12K and 3D TV channels in urban and rural areas
Solution
Deployment of announced Lower Earth Orbit (LEO) High Throughput Satellites (HTS) constellations by SpaceX, OneWeb, Samsung and LeoSat will create corresponding networks of around 10,000 satellites orbiting the planet. With high capacity, lower latency, small terminals and global coverage these networks will easily substitute any terrestrial network.
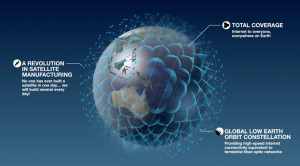
OneWeb Constellation (Source: http://spacenews.com/oneweb-satellites-to-settle-in-exploration-park-florida-with-eyes-on-business-beyond-oneweb/)
These constellations are inevitable and are backed by technology giants. Australia must adopt to the change and utilize maximum of the capacity from the networks, addressing all the above mentioned challenges with considerable lower CAPEX and OPEX. Australia can generate huge revenues as well by regulating the radio frequency allocations and by awarding licenses to local and foreign companies for providing the services. This change will be embraced happily by the public as well as they will be connected anywhere, anytime with best services and portable devices to eliminate limitations on mobility.